Power Modes
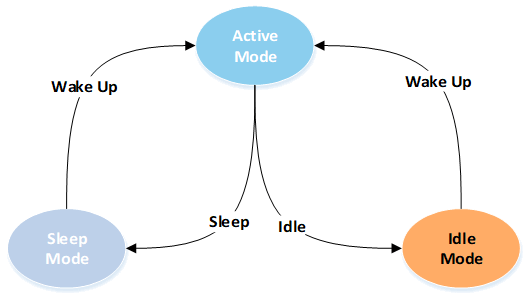
GR5525 SoCs operate in three power modes: active, idle, and sleep.
- Active mode
In this mode, the CPU operates at its full speed. Typical scenarios in this mode are described below:
- The MCU subsystem (including Arm processor, SRAM, and peripherals) remains in standby or active state.
- The Bluetooth subsystem (including RF transceiver and communication core) remains in standby or active state.
- The PMU subsystem (including DC/DC, LDO, and RTC) remains in active state.
- Idle mode
The idle mode is implemented by Wait For Interrupt/Wait For Event (WFI/WFE) command built in the Arm processor. When the WFI/WFE command is called, the program counter (PC) stays at the WFI/WFE command; when an interrupt request (IRQ) or an event occurs to wake up the CPU, the PC points to the next command and continues execution. The system detects the use of peripherals/Bluetooth subsystem/timers and decides whether to enter this mode.
- Sleep mode
In this mode, a high-frequency clock source HFXO_32M stops running; the MCU subsystem (except for Retention SRAM) and the Bluetooth subsystem are powered off. Only the always-on (AON) domains are powered on, to prevent data in Retention SRAM from getting lost, and to power the modules or I/Os that can wake up the system from sleep (including Bluetooth LE Timer, Sleep Timer, Real Time Calendar, and AON GPIOs). If there is no task to be processed, the system enters sleep mode.
The system automatically switches between the power modes, as shown in the figure below.