13-Bit SNSADC
Introduction
The Sense Analog-to-Digital Converter (SNSADC) is an ADC based on successive approximation registers (SARs). It is an 8-sensing-channel, 13-bit, 1 Msps ADC that can be used for single ended or for differential measurements. The SNSADC supports DMA to allow for large sample collection without overloading the MCU.
Main Features
- 13-bit analog-to-digital conversion
- 8-channel (MSIO_0–MSIO_7) analog-to-digital conversion
- Up to 16 MHz ADC clock frequency
- Up to 1 Msps conversion rate
- Single-ended or differential measurements
- Internal temperature and Vbattery sensors
- Ability to capture ADC samples using DMA, unburdening the MCU
- Programmable internal reference
Block Diagram

Resource Sharing
ADC and Comp can share the input channel from MSIO, but MSIO selected for Comp cannot be used at the same time for ADC sampling. The selection and configuration of I/Os can be found in the Pin Mux table.
Functional Description
The SNSADC can sample one of eight analog sources at a given time, using an input mux. Another two of the channel_N are used internally for VBAT and temperature monitoring for adjusting the analog and RF circuitry configurations for optimum performance. The SNSADC can be reconfigured to perform single-ended or differential measurements through the SNSADC_CFG.SINGLE_EN bit.
The reference voltage can be internally generated or supplied as one of the external inputs and can be selected through the SNSADC_CFG.REF_SEL field. The external reference source can be input through MSIO_0–MSIO_3, and the input voltage must not exceed half of the supply voltage.
The internal reference voltage can be programmed as 0.8 V, 1.2 V and 1.6 V through SNSADC_CFG.REF_VALUE field. For any specific reference value (Vref), the maximum ADC input is supposed to be approximately 2 x Vref, such as 1.85 x Vref. For example, in the case of Vref = 1.2 V, the maximum ADC input can be 2.25 V, which closely approximates 2.4 V. The minimum ADC input can be 0.
As shown in the following figure, the Iref comes from the relatively constant current generated by the chip bandgap module and will not be affected by other modules; it will generate different Vref levels by resistive voltage division.

The ADC sampling clock can be configured as 16 kHz, 8 kHz, 4 kHz, 16 MHz, 8 MHz, 4 MHz, or 1 MHz through the SENSE_ADC_CLK.WR field. The output value of the ADC will be stored into the FIFO, and users can transfer the data to RAM through DMA or MCU.
Raw Data Stream
- Pairs of successive 13-bit samples from SNSADC are combined into 32-bit words by aligning the 16-bit samples. 32-bit words are stored into an SNSADC FIFO of 64 entries, where each entry is 32-bit long and would hold two samples.
- When the SNSADC FIFO entry count reaches the 6-bit threshold value specified in the SENSE_FF_THRESH register, the samples stored in the FIFO are automatically streamed to the SRAM by using DMA controller. (DMA0 assigned to SNSADC must be programmed accordingly).
- The SNSADC FIFO status (not-empty signal and the entry count) can be polled in the SENSE_ADC_STAT register.
- The SNSADC FIFO can also be “popped” by one entry, by reading the SENSE_ADC_FIFO register.
Sample Operation Mode
The SNSADC supports two sample operation modes: single-ended measurement mode and differential measurement mode. Users can choose either of the modes by programming SINGLE_EN bit of SNSADC_CFG register.
- In single-ended measurement mode, the input signal should be assigned to channel N and the SNSADC will only measure the input signal of channel N. In this mode, larger voltage input indicates smaller raw data output. The input signal of channel N can be selected as MSIO_0–MSIO_7, temperature sensor, battery voltage sensor, or internal reference voltage by configuring the SNSADC_CFG.CH_N field. The raw data of the output is the measurement from channel N to GND and the allowed range of channel N is 0 to 2*Vref.
- In differential measurement mode, the input signals should be assigned to channel P and channel N and the SNSADC will measure the input signal of channel P minus channel N. The input signal of channel N is the same with that in single-ended measurement mode, and the input signal of channel P can be selected as MSIO_0–MSIO_7 or internal reference voltage by configuring the SNSADC_CFG.CH_P field. The raw data of the output is the measurement of difference voltage between channel P to channel N and the recommended range of channel P minus channel N is -1.8*Vref to 1.8*Vref.
Clock and Sampling Rate
- The SNSADC supports both fast sampling and slow sampling. If you need fast sampling, you can select 1M, 4M, 8M, or 16M ADC clock frequency. If you need slow sampling, you can select 16K, 8K, or 4K ADC clock frequency. The SNSADC clock can be selected by configuring the SENSE_ADC_CLK.WR field. The source of the SNSADC clock is shown in the figure below.
图 81 Source of SNSADC clock - It takes two clocks for the SNSADC to sample and hold data, and then 13 clocks to convert analog semaphore to 13-bit binary digits, totaling 15 clocks to generate one code. Therefore, the sampling rate of the SNSADC is 1/15 of the ADC clock frequency. For example, a 1 MHz ADC clock has a sampling rate of 66.7 ksps.
- The ADC sampling capacitor is 2 pF, which is affected by the RC circuit. If the external impedance is larger, the charging time of the capacitor will be longer. When a higher SNSADC sampling rate is set, it is likely to get abnormal raw data during sampling, because the capacitor is not fully charged. This can be solved by reducing the external impedance or reducing the SNSADC sampling rate.
Considerations for Using SNSADC
When using an internal reference source, it is necessary for users to ensure the stability of the reference source. The internal reference voltage is divided by the chip power supply voltage, so the reference source voltage of different gears has certain requirements for the chip power supply voltage. Insufficient chip supply voltage will lead to great ADC measurement error. The chip supply voltage range corresponding to the reference sources of different gears is as follows:
| Internal Reference | Chip Supply Voltage |
|---|---|
| 0P8V | 2.0 V to 3.63 V |
| 1P2V | 2.6 V to 3.63 V |
| 1P6V | 3.2 V to 3.63 V |
For the first data acquisition after SNSADC initialization, the SNSADC module needs to spend a cycle to clear the previous sampling parameters and another cycle to make the new sampling parameters effective. Therefore, when starting the SNSADC for the first time, the results of the first 2 to 3 pieces of 13-bit data may be unstable. It is recommended to filter out the first 2 to 3 pieces of 13-bit unstable data after SNSADC starts working.
Measuring MSIO Input
In single-ended mode:
Usually, the original value of 0–8191 corresponds to the voltage of 0–2*Vref, so the current voltage value is calculated by raw_data*lsb, where lsb is 2*Vref/8192. Due to the offset of the ADC itself, this correspondence is not accurate. the conversion relationship between output voltage and raw_data is as follows.
the slope and offset of the straight line are obtained by the method of linear fitting, and the current voltage can be converted by substituting the raw data. You need to obtain the slope and offset values during calibration based on different reference voltages. For more detailed information, refer to “Calibration”. The calibration values are stored in the exflash OTP.
As the offset and slope have been calibrated based on different reference voltages and stored in exflash OTP, the corresponding voltage value can be obtained from the raw data using the following formulas.
- In the exflash OTP, the slope_int_0p8 and offset_int_0p8 of the 0.8 V internal reference voltage are obtained by measuring the two input voltages and their corresponding raw data. You can use the following formula to convert the raw data into the current voltage value.
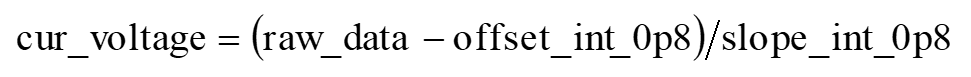
Similarly, exflash OTP also stores slope_int_1p2, offset_int_1p2 of the 1.2 V internal reference voltage, and slope_int_1p6, offset_int_1p6 of the 1.6 V internal reference voltage. When the internal 1.2 V reference voltage is selected, the raw data can be converted into the current voltage value by the following formula:
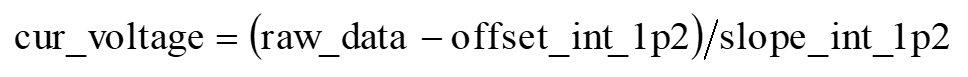
When the internal 1.6 V reference voltage is selected, the raw data can be converted into the current voltage value by the following formula:
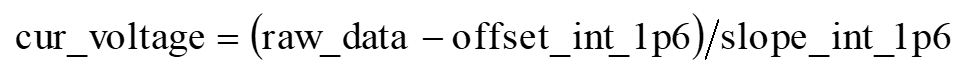
- The slope_ext_1p0 and offset_ext_1p0 of the external 1.0 V reference source are also stored in the exflash OTP. When the external reference voltage is selected, you only need to pay attention to the scaling of the slope_ext_1p0. The conversion formula is as follows:
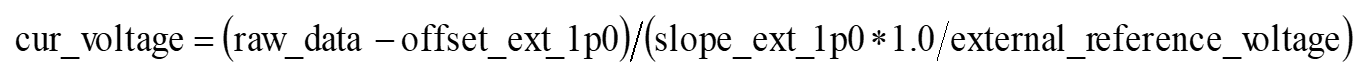
The above conversion formulas are used when the single-ended mode is selected.
In differential mode:
Usually, the original value of 8191-0 correspond to the voltage of -2*Vref – 2*Vref, so the slope in differential mode is -2 times of the slope in single-ended mode. In the differential mode, when both input channels are configured with internal reference voltage, i.e. the voltage being sampled is 0, the obtained raw_data is the offset value. Therefore, according to the obtained raw_data value, the calibration value obtained in single-ended mode is used to obtain the sampled voltage of the input.
- When 0.8 V internal reference voltage is selected, the calculation of input voltage values in dual-channel mode is as follows:
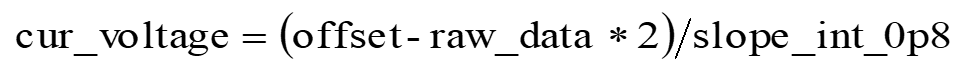
where "offset" refers to "raw_data", which is obtained by setting both input channels to internal reference voltage, and selecting internal reference voltage of 0.8 V.
- When 1.2 V internal reference voltage is selected, the calculation of input voltage values in dual-channel mode is as follows:
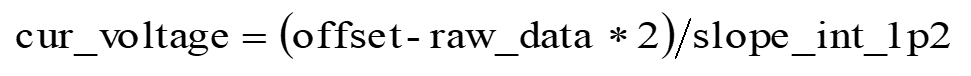
where "offset" refers to "raw_data", which is obtained by setting both input channels to internal reference voltage, and selecting internal reference voltage of 1.2 V.
- When 1.6 V internal reference voltage is selected, the calculation of input voltage values in dual-channel mode is as follows:
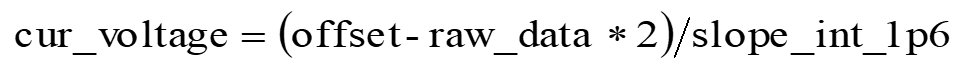
where "offset" refers to "raw_data", which is obtained by setting both input channels to internal reference voltage, and selecting internal reference voltage of 1.6 V.
- When 1.0 V external reference voltage is selected, the calculation of input voltage values in dual-channel mode is as follows:
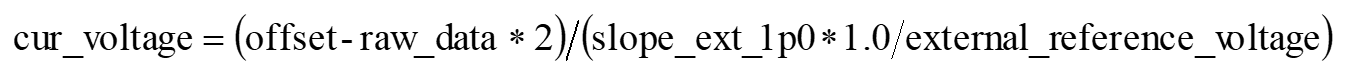
where "offset" refers to "raw_data", which is obtained by setting both input channels to internal reference voltage, and selecting external reference voltage of 1.0 V.
Measuring Battery Voltage
There is a voltage divider resistor inside the SoC to divide the voltage of the battery as VBAT/n. Users need to configure the SNSADC_CFG.CH_N field as 0xE (battery sensor as input), and select the internal reference voltage of 0.8 V.

Therefore, users can obtain the raw data of the current voltage, and then convert the raw data into the actual battery voltage value through the following formula:
Where, slope_int_0p8 and offset_int_0p8 are the slope and calibration offset when 0.8 V internal reference voltage is selected; n represents the divider ratio of the resistor to the battery voltage. With the change of temperature, this divider ratio will be slightly different, ranging from 3.85 to 3.855; the typical value of n is 3.854.
Measuring Internal Temperature
The device embeds a temperature sensor module, and the measurement range is from -40°C to 105°C. The temperature sensor converts the internal temperature of the chip into a voltage value as Vtemp and outputs it to the ADC for sample and conversion. After temperature calibration, the ADC converts the raw data into an actual temperature value.

If users want to measure the internal temperature of the chip, it is necessary to configure the SNSADC_CFG.CH_N field as 0xD (temperature sensor as input), and select the internal reference voltage of 0.8 V. Given temperature2 - temperature1 = [(raw_data2 - raw_data1) / slope), the calibration formula is as follows:
Where, temp_ref represents an ambient temperature during calibration; temp_offset represents ADC raw data at temp_ref ambient temperature during calibration.; slope_int_0p8 represents the calibrated slope value of the internal 0.8 V reference voltage; -0.00175 represents the amplification factor for the slope when used to measure temperature. In general, the output voltage decreases by a typical value of 1.863 mV for every 1 degree increase in temperature. The typical value of the voltage is 807.5 mV at -40°C and 583.9 mV at 80°C.
Calibration
Although some calibration values are provided to be stored in the exflah OTP at 3.3 V supply and normal temperature, these calibration values may have errors at other ambient temperatures. Users can use the following methods to recalibrate the conversion relationship between raw data and actual temperature or voltage.
- Single-ended mode calibration with internal reference source
- Select internal reference source by configuring the SNSADC_CFG.REF_SEL field, select internal reference level by configuring the SNSADC_CFG.REF_VALUE field, and select single-ended mode by configuring the SNSADC_CFG. SINGLE_EN bit to initialize ADC.
- Use a noise-free power supply to connect to the N terminal by configuring the SNSADC_CFG.CH_N field to start ADC sampling.
- Sample 1024 pieces of data and remove the maximum and minimum values to obtain the average of 1022 numbers.
- At this time, the average value is recorded as x0, and the input voltage is recorded as y0.
- Collect another voltage value using the above method, record the average code value as x1, and record the input voltage value as y1.
- Use the formula y = (x - offset) / slope, and bring in x0, y0, x1, y1 to obtain the offset and slope.
- The raw data can be converted into the actual voltage using the following formula:
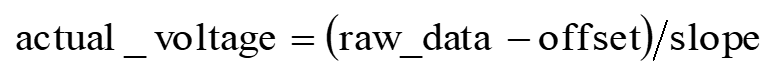
- Single-ended mode calibration with external reference source
- Select external reference source by configuring the SNSADC_CFG.REF_SEL field, and select single-ended mode by configuring the SNSADC_CFG. SINGLE_EN bit to initialize ADC.
- Use a noise-free power supply to connect to the N terminal by configuring the SNSADC_CFG.CH_N field to start ADC sampling.
- Use a noise-free power supply to connect to the ADC external input pin, and record the current external input as z (note that the external input is only connected from MSIO_0–MSIO_3).
- Sample 1024 pieces of data and remove the maximum and minimum values to obtain the average of 1022 numbers.
- At this time, the average value is recorded as x0, and the input voltage is recorded as y0.
- Collect another voltage value using the above method, record the average code value as x1, and record the input voltage value as y1.
- Use the formula y = (x - offset) / slope, and bring in x0, y0, x1, y1 to obtain the offset and slope.
- The raw_data can be converted into the actual voltage using the following formula:
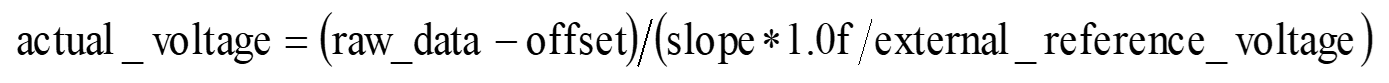
where external_refernce_voltage represents the voltage value of the external input as this time.
- Temperature sensor calibration
- Select internal reference source by configuring the SNSADC_CFG.REF_SEL field, and select internal 0.8 V reference source by configuring the SNSADC_CFG.REF_VALUE field.
- Select single-ended mode by configuring the SNSADC_CFG. SINGLE_EN bit, and select temperature as N-terminal input by configuring the SNSADC_CFG.CH_N field to initialize ADC.
- Put the chip into a constant temperature environment.
- Sample1024 pieces of data and remove the maximum and minimum values to obtain the average of 1022 numbers.
- At this time, the average value is recorded as temp_offset , and the current temperature is recorded as temp_ref.
- Given temperature2 - temperature1 = [(raw_data2 - raw_data1) / slope), and the slope = (slope_int_0p8*2)/(-0.00175), the raw data can be converted into the actual temperature using the following formula:
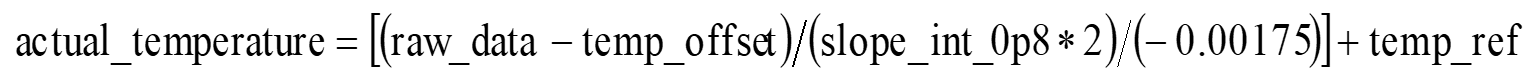
Registers
SNSADC_CFG
- Name: Sense ADC Configuration Register
- Description: This register is used to configure reference, channels, and input mode of ADC.
- Base Address: 0x4000A800
- Offset: 0x00
- Reset Value: 0x0710070A
| Bits | Field Name | RW | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 31 | MAS_RST | RW | 0x0 | Reset SNSADC master. Value:
|
| 30 | EN | RW | 0x0 | Enable SNSADC. Value:
|
| 29:27 | REF_SEL | RW | 0x0 | Reference voltage select Value:
Note: Because the maximum input for any MSIO is supposed to be VBAT, there is no benefit from using an external input higher than VBAT/2. |
| 26:24 | REF_HP | RW | 0x7 | Used to define the current in the reference circuit: 0x0: 100 ksps 0x7: 1 Msps |
| 23:20 | CH_P | RW | 0x1 | Used to define input for channel P: Value:
|
| 19:16 | CH_N | RW | 0x0 | Used to define input for channel N: Value:
|
| 15 | TEMP_EN | RW | 0x0 | Enable temperature sensor. Value:
|
| 14 | VBAT_EN | RW | 0x0 | Enable battery sensor. Value:
|
| 13 | SINGLE_EN | RW | 0x0 | Used to define operation to either single ended or differential mode. Value:
|
| 12 | OFS_CAL_EN | RW | 0x0 | Used to swap inputs of comparator for offset calibration. Value:
|
| 11 | RSVD | R | Reserved bit | |
| 10:8 | DYMAMIC | RW | 0x7 | Used to define dynamic range of ADC. Default: 0x7; for higher input signal frequencies close to Nyquist rate, use 0x1. |
| 7:4 | RSVD | R | Reserved bits | |
| 3:0 | REF_VALUE | RW | 0xA | Buffered internal reference Value:
Note: For any specific reference value (Vref), the maximum ADC input is supposed to be 2 x Vref. |
SENSE_ADC_FIFO
- Name: Sense ADC FIFO Output Register
- Description: Reading this register will pop an entry from the sense ADC FIFO.
- Base Address: 0x4000E000
- Offset: 0x00
- Reset Value: 0x00000000
| Bits | Field Name | RW | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
31:0 |
DATA |
R |
0x0 |
When the register is read, data in the FIFO buffer is accessed. |
SENSE_FF_THRESH
- Name: Sense ADC FIFO Control Register
- Description: This register is used to enable DMA request and set the threshold at which the DMA request is made to the hardware handshake mechanism.
- Base Address: 0x4000E000
- Offset: 0x004
- Reset Value: 0x00000000
| Bits | Field Name | RW | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
31:17 |
RSVD |
R |
Reserved bits |
|
16 |
DMA_EN |
RW |
0x0 |
|
15:6 |
RSVD |
R |
Reserved bits |
|
5:0 |
THRESH |
RW |
0x0 |
This is used to set the threshold at which the DMA request is made to the hardware handshake mechanism, should be a power of 2. |
SENSE_ADC_STAT
- Name: Sense ADC Status Register
- Description: This register contains the number of valid data entries in the ADC FIFO memory.
- Base Address: 0x4000E000
- Offset: 0x008
- Reset Value: 0x00000000
| Bits | Field Name | RW | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
31:17 |
RSVD |
R |
Reserved bits |
|
16 |
FLUSH |
W |
Write 1 to flush FIFO DATA. |
|
15:9 |
RSVD |
Reserved bits |
||
8 |
VAL |
R |
0x0 |
Identify whether FIFO is empty. Value:
|
7 |
RSVD |
R |
Reserved bit |
|
6:0 |
COUNT |
R |
0x0 |
Sense ADC FIFO Count, number of 32-bit words in the FIFO. Maximum value is 0x40 or decimal 64. |
SENSE_ADC_CLK
- Name: Sense ADC Clock Register
- Description: This register selects ADC clock.
- Base Address: 0x4000E000
- Offset: 0x00C
- Reset Value: 0x00000000
| Bits | Field Name | RW | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 31:19 | RSVD | R | Reserved bits | |
| 18:16 | RD | R | Actual clock select value | |
| 15:3 | RSVD | R | Reserved bits | |
| 2:0 | WR | RW | 0x0 | SNSADC clock selection Value (Hz):
|
SENSE_ADC_GET_TKN_HW
- Name: Sense ADC Get Hardware Token Register
- Description: Read this register to try to get token for Hardware and return the result of the trial.
- Base Address: 0x4000E000
- Offset: 0x014
- Reset Value: 0x00000000
| Bits | Field Name | RW | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
31:9 |
RSVD |
R |
Reserved bits |
|
8 |
HW_OWNER |
R |
0x0 |
|
7:1 |
RSVD |
R |
Reserved bits |
|
0 |
HW_LOCKED |
R |
0x0 |
|
SENSE_ADC_GET_TKN_SW
- Name: Sense ADC Get Software Token Register
- Description: Read this register to try to get token for software and return the result of the trial.
- Base Address: 0x4000E000
- Offset: 0x018
- Reset Value: 0x00000000
| Bits | Field Name | RW | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
31:9 |
RSVD |
R |
Reserved bits |
|
8 |
SW_OWNER |
R |
0x0 |
|
7:1 |
RSVD |
R |
Reserved bits |
|
0 |
SW_LOCKED |
R |
0x0 |
|
SENSE_ADC_RET_TKN_HW
- Name: Sense ADC Release Hardware Token Register
- Description: Write any value to this register to release the Hardware token.
- Base Address: 0x4000E000
- Offset: 0x01C
- Reset Value: 0x00000000
| Bits | Field Name | RW | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
31:1 |
RSVD |
R |
Reserved bits |
|
0 |
HW_RELEASE |
W |
0x0 |
Write any value to this bit to release the HW token. |
SENSE_ADC_RET_TKN_SW
- Name: Sense ADC Release Software Token Register
- Description: Write any value to this register to release the software token.
- Base Address: 0x4000E000
- Offset: 0x020
- Reset Value: 0x00000000
| Bits | Field Name | RW | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
31:1 |
RSVD |
R |
Reserved bits |
|
0 |
SW_RELEASE |
W |
0x0 |
Write any value to this bit to release the SW token. |
SENSE_ADC_GET_TKN_STS
- Name: Sense ADC Token Status Register
- Description: This register indicates the token status and the token owner.
- Base Address: 0x4000E000
- Offset: 0x024
- Reset Value: 0x00000000
| Bits | Field Name | RW | Reset | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
31:9 |
RSVD |
R |
Reserved bits |
|
8 |
OWNER |
R |
0x0 |
|
7:1 |
RSVD |
R |
Reserved bits |
|
0 |
LOCKED |
R |
0x0 |
|
Reading this register would not issue any action of getting a token.
Electrical Specifications
All the data in the following table are obtained under the conditons: VBAT=3.3 V and VREF = 1.6 V.
| Parameter | Symbol | Min. | Typ. | Max. | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical number of bits | PNOB | 13 | bit | ||
| Sampling clock frequency | Freq | 4K | 16M | Hz | |
| Integrated nonlinearity | INL | -8 | 8 | LSB | |
| Differential nonlinearity | DNL | -8 | 8 | LSB | |
| Signal-to-noise and distortion ratio | SNDR | 60[1] | dB | ||
| Total harmonic distortion | THD | 65[1] | dB | ||
| Effective number of bits | ENOB | 9.5[1] | bit | ||
| Differential offset voltage, 13-bit resolution | Vos | -4 | 4 | LSB | |
| Gain error | Eg | -1 | 1 | % | |
| Sampling capacitor | Cs | 2 | pF | ||
| Sampling rate | F_S | 0.27 | 1067 | ksps | |
| Input resistance | Rin | Hi-Z | ohm | ||
| Current consumption during ADC conversion @100 Ksps | I_ADC | < 20 | μA | ||
| Spurious free dynamic range | SFDR | 68[1] | dB |
[1]The data of SNDR, THD, ENOB, and SFDR in the table are obtained under the following specified test conditions: sampling clock frequency = 1 MHz, signal frequency = 1 kHz, and signal amplitude = 1.85*VREF.


